Printed fabric, a significant element in the textile industry, has evolved considerably since its inception. Today, several primary techniques are used in printing fabrics, each with its unique process, advantages, and applications, reflecting the rich history and technological advancements in textile printing.
One of the most enduring methods is screen printing, a technique that uses a stencil (or screen) for each color in the design. Ink is pushed through the screen onto the fabric, producing vibrant and durable colors. This method is particularly cost-effective for large runs, making it ideal for t-shirts, posters, and other apparel. The high color vibrancy and durability of screen-printed fabrics contribute to their popularity, as these qualities enhance the visual appeal and longevity of the items, providing consumers with both aesthetic and practical benefits.
Digital printing represents a more modern approach, utilizing large-format inkjet printers to apply designs directly onto the fabric. This technique allows for high-resolution, detailed designs with unlimited color options, making it perfect for small batches and custom designs. The flexibility and precision of digital printing enable the production of intricate patterns and images that were previously unattainable with traditional methods. This has significantly enriched people's material life enjoyment, as the variety and beauty of printed fabrics are now more accessible than ever.
In heat transfer printing, designs are printed onto special transfer paper using sublimation inks and then heat-pressed onto the fabric. This method is particularly advantageous for small batches and custom items, as it allows for detailed and vibrant prints. Common applications include sportswear, custom t-shirts, and promotional items. The ability to produce high-quality prints on demand has made heat transfer printing a valuable tool for businesses catering to niche markets and personalized products.
Block printing is a traditional method where designs are carved onto wooden blocks, which are then dipped in dye and stamped onto the fabric. This artisanal technique produces unique, handcrafted designs and is ideal for small-scale production. Despite its labor-intensive nature, block printing continues to be cherished for its ability to create distinct and culturally rich patterns, often seen in traditional textiles and home decor items.
Rotary screen printing is an adaptation of screen printing that uses cylindrical screens. The fabric passes through the rotating screen, allowing for continuous patterns to be applied efficiently. This method is suitable for high-volume production, making it a staple in manufacturing fabrics for clothing, home textiles, and industrial applications. The efficiency and scalability of rotary screen printing ensure that the benefits of printed fabrics—diverse patterns, aesthetic appeal, and practicality—are available to a wide audience.
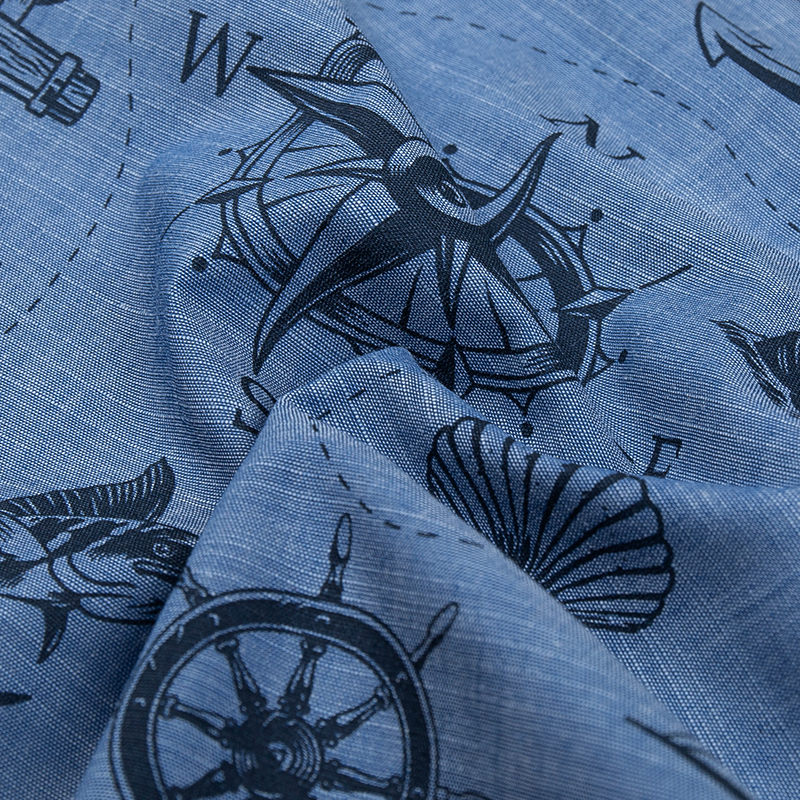

Discharge printing involves using a chemical to remove color from dyed fabric, creating a design by subtracting the dye. This technique is particularly effective on dark fabrics, producing soft prints with no added weight. Commonly used in fashion textiles, discharge printing offers a unique way to create intricate and multi-colored patterns that stand out.
Resist printing employs a resist paste (such as wax) to prevent dye from penetrating certain areas of the Printed fabric. After dyeing, the resist is removed, revealing the pattern. This method is known for creating complex and multi-colored designs, often seen in traditional textiles like batik and tie-dye fabrics. The cultural and artistic significance of resist printing adds a layer of historical and aesthetic value to the fabric.
Lastly, Direct to Garment (DTG) printing is similar to digital printing but is specifically designed for garments. This method allows for detailed, high-quality prints with unlimited colors, suitable for small batches and custom designs. DTG printing has become increasingly popular for custom t-shirts, hoodies, and other apparel, offering businesses and consumers the ability to create personalized and fashionable items.
In conclusion, the primary techniques used in printing fabrics today—screen printing, digital printing, heat transfer printing, block printing, rotary screen printing, discharge printing, resist printing, and DTG printing—each offer distinct advantages that enhance the quality, variety, and accessibility of printed fabrics. These methods not only address the practical needs of production but also significantly enrich the aesthetic and material enjoyment of people's lives. The evolution and diversification of fabric printing techniques continue to drive innovation in the textile industry, reflecting both historical traditions and modern advancements.



 English
English Español
Español Jul 25,2024
Jul 25,2024














 +86-519-86503571
+86-519-86503571
 Phone: +86-13218666905
Phone: +86-13218666905 Tel: +86-0519-86503571
Tel: +86-0519-86503571 Fax: +86-0519-86508551
Fax: +86-0519-86508551 E-mail:
E-mail: 